
Behaviorism, Cognitivism & Constructivism
Behaviourism: The behaviourist view is quite comprehensive and includes a variety of thoughts, but all these thoughts suggest a common approach to learning in terms of the development of connections between stimuli received and responses displayed by organisms/learners. Behaviourists have conceived of teaching as a manipulation of the environment in order to produce desired behavioural changes & learners and thus make education more effective.
Cognitivism: The cognitive school views (1) learning as an active process “involving the acquisition or reorganization of the cognitive structures through which humans process and store information”. This theory describes knowledge acquisition as a mental activity involving internal coding and structuring by the learner and suggests that learning happens best under conditions that are aligned with human cognitive architecture. Instruction should be based on a student’s existing mental structures or schema to be effective.
Constructivism: This term refers to the idea that learners construct knowledge for themselves; each learner individually (and socially) constructs meaning-as he or she learns. Constructing meaning is learning; there is no other kind. The dramatic consequences of this view are twofold; 1) we have to focus on the learner in thinking about learning (not on the subject/lesson to be taught): 2) There is no knowledge independent of the meaning attributed to experience (constructed) by the learner, or community of learners.
Multiple Intelligences
Howard Gardner found that people have more than one way of processing information and that a typical IQ score doesn’t completely measure intelligence. He created the theory of Multiple Intelligences which elaborates that every person’s level of intelligence actually consists of many distinct “intelligences”; to include:
- Verbal-linguistic intelligence (well-developed verbal skills and sensitivity to the sounds, meanings and rhythms of words)
- Logical-mathematical intelligence (ability to think conceptually and abstractly, and capacity to discern logical and numerical patterns)
- Spatial-visual intelligence (capacity to think in images and pictures, to visualize accurately and abstractly)
- Bodily-kinesthetic intelligence (ability to control one’s body movements and to handle objects skillfully)
- Musical intelligences (ability to produce and appreciate rhythm, pitch and timber)
- Interpersonal intelligence (capacity to detect and respond appropriately to the moods, motivations and desires of others)
- Intrapersonal (capacity to be self-aware and in tune with inner feelings, values, beliefs and thinking processes)
- Naturalist intelligence (ability to recognize and categorize plants, animals and other objects in nature)
- Existential intelligence (sensitivity and capacity to tackle deep questions about human existence such as, “What is the meaning of life? Why do we die? How did we get here?”

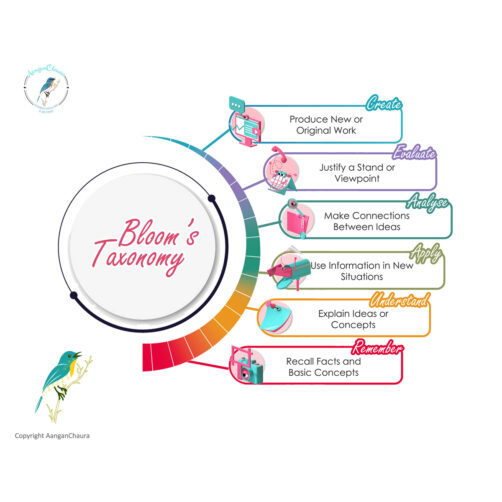
Bloom's Taxonomy of Cognitive Development
Bloom’s Taxonomy Is a framework which provides hierarchical ordering of cognitive skills, hence of immense use while forming Learning Objectives for learners to learn better.
Remembering of information which has previously been learned and ranging from a recall of specific facts to recalling theories.
Understanding in turn amounts to interpretation or translation of the material to arrive at a prognosis of consequences.
Applying implies use of what has been learnt in new similar or variant situations; application of concepts, principles, methods, laws, theories etc.
Analyzing implies breaking down the information available into its component parts to understand it in detail, understanding the relativity between the component parts and identification of the principles involved.
Evaluating is the judgement of the work of the material for the purpose for which it is intended.
Creating involves the “putting together of elements and parts so as to form a whole”; Generating, planning, producing and putting the components together to form a new structure.

Behaviorism, Cognitivism & Constructivism
Behaviourism: The behaviourist view is quite comprehensive and includes a variety of thoughts, but all these thoughts suggest a common approach to learning in terms of the development of connections between stimuli received and responses displayed by organisms/learners. Behaviourists have conceived of teaching as a manipulation of the environment in order to produce desired behavioural changes & learners and thus make education more effective.
Cognitivism: The cognitive school views (1) learning as an active process “involving the acquisition or reorganization of the cognitive structures through which humans process and store information”. This theory describes knowledge acquisition as a mental activity involving internal coding and structuring by the learner and suggests that learning happens best under conditions that are aligned with human cognitive architecture. Instruction should be based on a student’s existing mental structures or schema to be effective.
Constructivism: This term refers to the idea that learners construct knowledge for themselves; each learner individually (and socially) constructs meaning-as he or she learns. Constructing meaning is learning; there is no other kind. The dramatic consequences of this view are twofold; 1) we have to focus on the learner in thinking about learning (not on the subject/lesson to be taught): 2) There is no knowledge independent of the meaning attributed to experience (constructed) by the learner, or community of learners.

Multiple Intelligences
Howard Gardner found that people have more than one way of processing information and that a typical IQ score doesn’t completely measure intelligence. He created the theory of Multiple Intelligences which elaborates that every person’s level of intelligence actually consists of many distinct “intelligences”; to include:
- Verbal-linguistic intelligence (well-developed verbal skills and sensitivity to the sounds, meanings and rhythms of words)
- Logical-mathematical intelligence (ability to think conceptually and abstractly, and capacity to discern logical and numerical patterns)
- Spatial-visual intelligence (capacity to think in images and pictures, to visualize accurately and abstractly)
- Bodily-kinesthetic intelligence (ability to control one’s body movements and to handle objects skillfully)
- Musical intelligences (ability to produce and appreciate rhythm, pitch and timber)
- Interpersonal intelligence (capacity to detect and respond appropriately to the moods, motivations and desires of others)
- Intrapersonal (capacity to be self-aware and in tune with inner feelings, values, beliefs and thinking processes)
- Naturalist intelligence (ability to recognize and categorize plants, animals and other objects in nature)
- Existential intelligence (sensitivity and capacity to tackle deep questions about human existence such as, “What is the meaning of life? Why do we die? How did we get here?”

Bloom's Taxonomy of Cognitive Development
Bloom’s Taxonomy Is a framework which provides hierarchical ordering of cognitive skills, hence of immense use while forming Learning Objectives for learners to learn better.
Remembering of information which has previously been learned and ranging from a recall of specific facts to recalling theories.
Understanding in turn amounts to interpretation or translation of the material to arrive at a prognosis of consequences.
Applying implies use of what has been learnt in new similar or variant situations; application of concepts, principles, methods, laws, theories etc.
Analyzing implies breaking down the information available into its component parts to understand it in detail, understanding the relativity between the component parts and identification of the principles involved.
Evaluating is the judgement of the work of the material for the purpose for which it is intended.
Creating involves the “putting together of elements and parts so as to form a whole”; Generating, planning, producing and putting the components together to form a new structure.

